Thumb sucking is a prevalent behavior among infants and young kids. Although harmless in the early stages, prolonged thumb sucking can have negative effects on both dental health and overall development. It is crucial to address this habit early to prevent any potential issues. In this article, we will delve into the consequences of thumb-sucking on dental health and offer effective strategies to help children break this habit.
Understanding Thumb Sucking
Thumb sucking is a natural reflex that provides comfort and security to infants. Most children naturally stop this habit between the ages of two and four. However, if it persists beyond this age, it can lead to various dental complications.
Reasons for Thumb Sucking
Children engage in thumb sucking for various reasons, including seeking comfort, self-soothing during stress, forming a habit from infancy, or out of boredom or inactivity.
Impact of Thumb Sucking on Dental Health
Prolonged thumb sucking can significantly impact a child’s dental health. Understanding these potential issues can serve as motivation for parents to address the habit promptly.
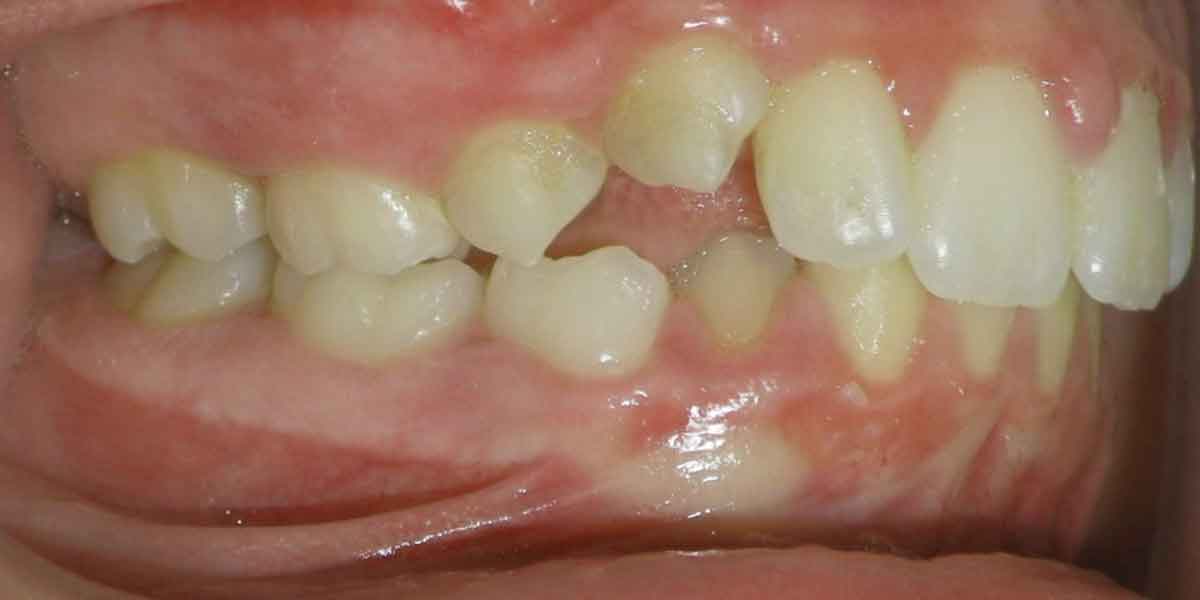
Dental Misalignments
Thumb sucking can cause malocclusion, which refers to teeth misalignment. This can result in protruding upper front teeth (overbite) or inwardly tilted lower teeth (underbite), affecting chewing, speech, and self-esteem.
Palate Deformation
Continuous thumb sucking can affect the development of the palate, leading to a high, narrow palate that can cause breathing difficulties and improper teeth alignment.
Speech Impediments
Dental misalignments and palate deformation from thumb sucking can contribute to speech problems, such as lisps, impacting a child’s communication skills and social interactions.
Skin Irritation
Chronic thumb sucking can lead to skin irritation, calluses, or infections on the thumb, causing discomfort and potentially requiring medical attention.
Effective Strategies to Break the Thumb Sucking Habit
Breaking the thumb-sucking habit may be challenging, but with patience and consistency, it is achievable. Here are some effective strategies to help children overcome this habit.
Positive Reinforcement
Using positive reinforcement, such as praise and rewards for not sucking their thumb, can encourage behavior change. Implementing a reward chart can track progress and motivate the child.
Identify Triggers
Understanding the triggers for thumb sucking can help address the root cause. By identifying patterns and providing alternative comfort or distraction methods during these times, parents can help children overcome the habit.
Gentle Reminders
Gently reminding children not to suck their thumb can increase awareness of the habit. Using calm and gentle reminders, along with offering substitute activities, can encourage them to stop without creating anxiety.
Provide Comfort and Security
If thumb sucking is a way for children to self-soothe, offering alternative sources of comfort, such as cuddles, favorite blankets, or special toys, can help them feel secure without resorting to thumb-sucking.
Use a Thumb Guard
Thumb guards are plastic devices that make thumb sucking difficult. Using them consistently and explaining their purpose to the child can help break the habit without feelings of punishment.
Seek Professional Help
If efforts to stop thumb sucking are unsuccessful, seeking help from a pediatric dentist, orthodontist, or therapist may be beneficial. They can provide additional strategies or appliances to discourage thumb-sucking and address any underlying emotional issues.
Conclusion
Thumb sucking is a common habit among young children that can lead to dental and developmental issues if prolonged. By employing positive reinforcement, identifying triggers, providing comfort, and seeking professional help, parents can help children break this habit and safeguard their dental health. With patience and consistency, children can overcome thumb sucking and enjoy a healthier, happier smile.